About Treatment
The brain is the most important part of the human central nervous system. Together with the spinal cord, which is located in the spinal column, they control all the organs and systems of our body. Both the brain and the spinal cord are connected to the rest of the body through nerves - cranial and spinal. The brain is responsible for functions such as vision, touch, smell and hearing.
The human brain consists of nerve cells - neurons, which are interconnected by special processes. The brain itself consists of two hemispheres - the right and left, cerebellum and brain stem. Each of these parts has its own functions, for example, the cerebellum is responsible for the coordination of movements, and in the brain stem there are vital centers of respiration and cardiac activity. The brain stem then passes into the spinal cord, which is located in the spinal canal.
Between the brain and spinal cord is the so-called brain stem. It contains centers that are responsible for functions such as heartbeat and breathing and some others.
Nutrition of the brain is carried out both through blood vessels, and cerebrospinal fluid - a transparent liquid with a certain composition. It washes the brain and circulates in its cavities, so-called ventricles of the brain. The brain and spinal cord itself are covered with meninges - soft and hard.
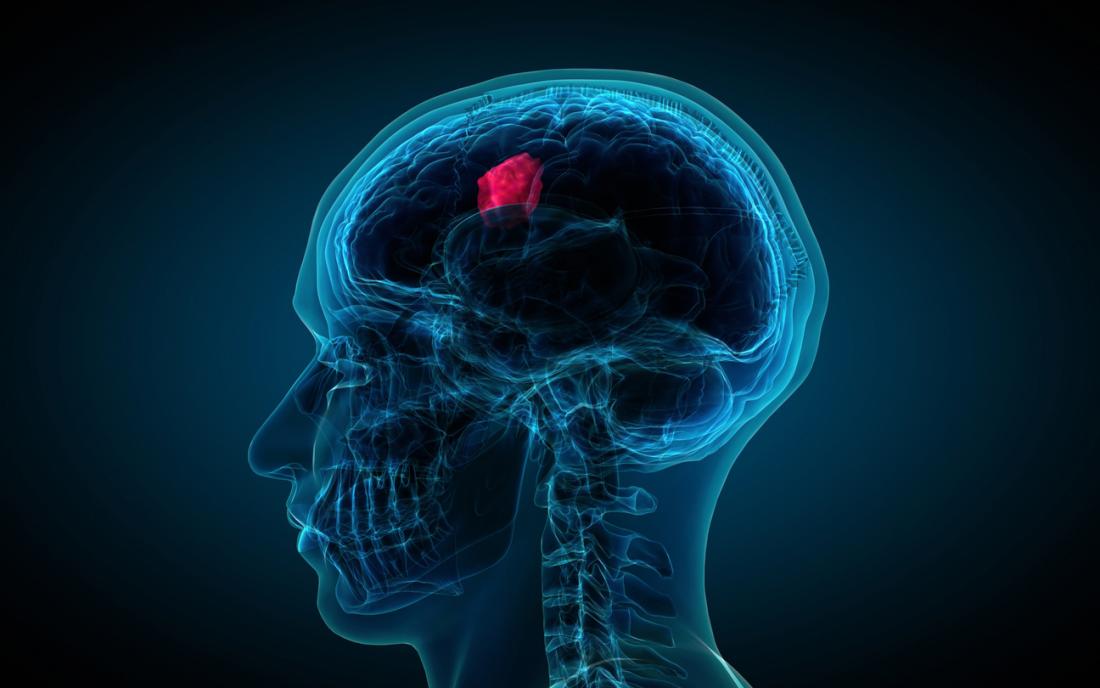
The brain - the structure is fragile and delicate, so nature has reliably enclosed it completely in the bone frame - the skull, protecting it from injuries and environmental influences. However, the disadvantage of such protection is that any pathological process in the brain - infection, hemorrhage or tumor - leads to compression of the brain tissue. That is why the nature of the brain tumor is not so important - benign or malignant, like what area it is in and how much it compresses the brain.
Treatment of brain tumor should be individual. The methods of treatment depend on factors such as age, general health and the presence of concomitant diseases, as well as the size, location and type of tumor.
Surgical treatment of brain tumors
In most cases of brain tumors, surgical treatment is performed. The purpose of surgical treatment is to identify tumor and its surgical removal. If tumor is located in a place in the brain that cannot be removed, surgeon performs a biopsy to determine the type of tumor.
In some cases, most of them with benign tumors, surgical removal of the tumor can completely eliminate the symptoms of the disease. If possible, neurosurgeon tries to remove the entire tumor.
The difference from surgical interventions during conventional abdominal operations for malignant tumors is that in those cases surgeon can excise not only the tumor, but also grabbing healthy tissue along the edges, minimizing the risk of tumor recurrence. In the case of the brain, this is not possible, since every millimeter of the brain is responsible for certain functions of the body.
If the tumor blocks the free flow of cerebrospinal fluid, or impedes the movement of blood through the vessels, then as a preoperative preparation, shunting can be performed - the system of flexible tubes, which will play the role of artificial cerebrospinal fluid, can be performed. Operation is performed under the control of MRI.
Direct removal of a brain tumor can be performed:
with a scalpel;
laser: it will evaporate the mutated cells using high temperature;
ultrasound: the tumor is divided into small pieces with a high-frequency sound, after which each of them is removed from the cranial cavity by suction by pressure. Possible only on confirmed benign tumors;
radio knife: in addition to evaporation of the tumor tissue, which immediately stops tissue bleeding, the nearby brain areas are irradiated with gamma rays.
Today, in the treatment of brain tumors, as well as other pathological formations, such as cysts, hematomas after traumatic brain injuries, etc. endoscopic surgery is used. Endoscopic intervention is an intervention without wide incisions, using special endoscopic techniques. In addition, fluid can be evacuated endoscopically from the ventricles of the brain in children with hydrocephalus (ventriculoscopy).
-
Types of Brain Tumors
Astrocytoma
Glioma
Ependymoma
Oligodendroglioma
Medulloblastoma
Meningioma
Schwanoman
Craniopharyngeoma
Swollen areas of the pineal gland. -
Diagnostics
CT
MRI -
Types of Operation
Stereosurgery
Craniotomy
Endoscopy
-
Necessary actions before surgery
Decreasing intracranial pressure
Biopsy
State stabilization
Magnetic resonance or computed tomography
Electrocardiogram
Aangiography
Urine and Blood tests
Fluorography
-
Rehabilitation Period
2-4 months
Symptoms of brain cancer are extensive, and often not taken seriously. But if at least two of the listed list are found, it is worth contacting specialists.
Severe, regular headache
Dizziness
Vomiting
Nausea
Memory and speech problems
Problems with coordination of movements, balance
Sharp visual problems
Noticeable changes in behavior: aggression, tearfulness, irritability.
In children, the main cause of tumors is change of the structure of the genes responsible for the proper formation of the nervous system, or the appearance of one or more pathological oncogenes that are responsible for controlling the life cycle of cells in the structure of normal DNA. Such anomalies can be congenital, can also appear in the immature brain.
Congenital changes occur in these genes:
NF1 or NF2. This causes Recklingausen syndrome, which in ½ cases is complicated by the development of pilocytic astrocytoma;
ARC. Its mutation leads to Turco syndrome, and leads to medulloblastoma and glioblastoma — malignant tumors;
RTCH, changing in which leads to Gorlin's disease, and it is complicated by neuromas;
P53, associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome, which is characterized by the appearance of various sarcomas - malignant non-epithelial tumors, including in the brain;
some other genes.
Triggers
When the brain is predisposed to formation of a tumor, or there is a decrease in the rate of damage recovery, then the follwing factors can provoke (and in adults initially cause) the formation of a tumor:
ionizing radiation;
electromagnetic waves;
infrared radiation;
exposure to vinyl chloride gas, which is needed in the manufacture of plastic materials;
pesticides;
GMOs in food;
human papillomatosis viruses of types 16 and 18 (they can be diagnosed by blood PCR, and their treatment is to maintain immunity at a good level)
More likely to "get" the formation in the cranial cavity in:
men
people under the age of 8 or 65-79;
Chernobyl liquidators;
those who constantly carry a mobile phone near their heads or talk on it (even through a hands-free device);
working in a toxic plant when contact occurs with mercury, refined products, lead, arsenic, pesticides;
if organ transplantation was performed;
HIV infected
receiving chemotherapy for a tumor of any localization.
The recovery of a person after surgical or alternative treatment of a brain tumor depends on those functions that have been inhibited. So, in case of impaired motor function, limb massage, physiotherapy, exercise therapy are necessary. If problems have occurred with hearing, classes are conducted with an audiologist, drugs are prescribed to improve communication between brain neurons.
The rehabilitation process involves specialists:
neurosurgeon;
radiation oncologist;
oncologist;
speech therapist;
neurologist;
psychologist;
ophthalmologist;
physiotherapist.
More often complications appear after open excision of a brain tumor:
loss of functions of the part of the brain in which the operation is carried out;
incomplete excision of the tumor - may require repeated surgical intervention;
infection of the wound and the penetration of pathogens into the brain tissue;
side effects associated with intracranial bleeding;
cerebral edema, which leads to epileptic seizures, hypoxia and circulatory disorders;
decreased visual acuity or its complete loss;
impaired motor function (partial or complete paralysis);
disorders of the vestibular apparatus;
partial or complete amnesia (short-term, long-term);
effect on the urination process;
the appearance of symptoms of mental disorders;
speech problems.
Surgical intervention to remove tumor lesions is necessary when:
the location of the tumor is the accessible area, and the likelihood of complications is much lower than if the operation is not performed;
there is no further growth of neoplasms of a benign nature, but their negative impact on the performance of brain structures is noted;
there is evidence that the tumor is malignant;
the condition and age category of the patient allow surgery.
Among the contraindications to the use of surgical intervention, the following are distinguished:
inoperable tumor (neoplasm is located in a place inaccessible for removal);
exhaustion of the body against the background of pathological processes or age-related changes;
malignant neoplasm that grows in the surrounding tissue;
the prognosis of survival as a result of the operation is not so favorable than without it;
if patient rejects the operation.