About Treatment
If the skin lesion enlarges, ulcerates, bleeds, or does not heal, it should be suspected of being malignant. Diagnosis must be confirmed with biopsy. Any element is suitable for biopsy. It is important to prevent sun exposure using sunscreen, protective clothing and hats.
Skin Cancer Causes
The appearance of any malignant neoplasm is a consequence of malfunction in the body: normally, the immune system destroys defective cells before they begin to divide uncontrollably. If, for some reason, the defense mechanisms do not work, tumor grows in size and becomes invulnerable to biologically active substances and killer cells.
In the case of skin cancer, the most dangerous environmental factors that increase the likelihood of tumor development are ultraviolet and ionizing radiation, as well as exposure to harsh chemicals. Therefore, such malignant tumors are often detected in people who have had contact with radiation or worked in the chemical industry. Experts note that skin cancer is often triggered by visiting a tanning salon: the fashion for bronze tanning has led to a significant increase in the incidence of malignant neoplasms in women.
Symptoms and Signs of Skin Cancer
Any type of malignant tumors first shows itself locally - at the site of the lesion, and then, if untreated, affects patient's well-being as a whole.
Local symptoms of skin cancer are visible: it can be a wound that does not heal for several weeks, a spot that gradually increases in size, or a mole that has changed its shape or color. Depending on the type of tumor, the growth of the neoplasm is slow or fast, but in any case, the change in the skin progresses. Redness, itching, pain, bleeding, or peeling are common in the affected area. It is important to know that skin cancer can develop, including on the mucous membranes - in the mouth or in the nasal cavity, as well as under the hair on the head.
Common symptoms appear in all types of cancer in the same way: loss of appetite, chronic fatigue, weight loss, periodic episodes of an unreasonable rise in temperature to subfebrile degrees (about 37.5 ° C).
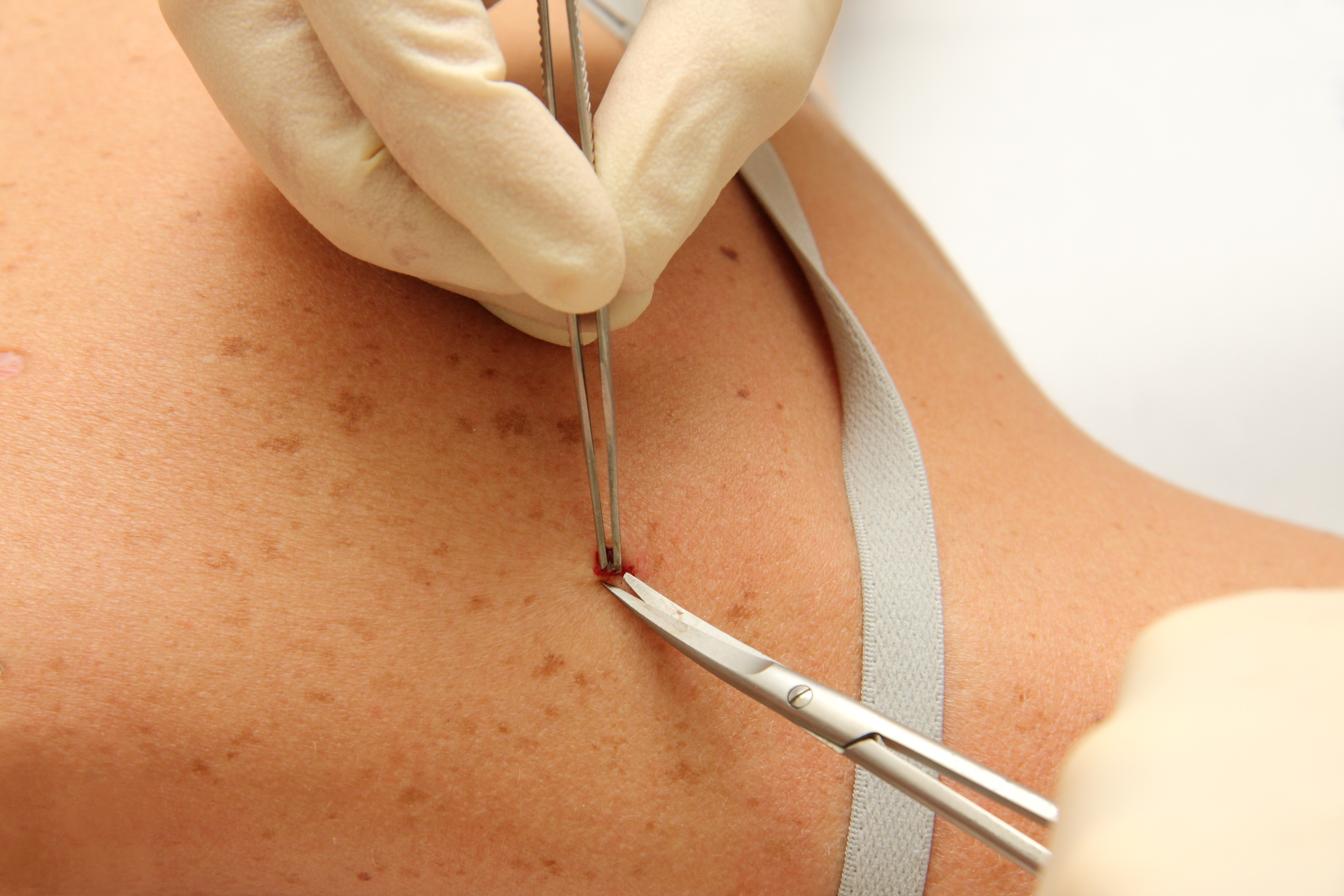
Performing surgery to remove a malignant tumor
Tumor spreads to surrounding tissue. Therefore, during the operation, not only tumor formation itself is removed, but also some of the tissues around it, in order to prevent relapse. This prevents the development of metastases and gives a chance for a complete cure.
The most important tool during the operation is scalpel. Over time, they began to use an ultrasonic scalpel, a radio frequency knife, a laser beam. With the help of modern instruments, you can avoid large blood loss, as well as reduce the time for subsequent recovery.
For the operation to be successful, surgeons must be extremely careful. To avoid a cancerous process, doctors must follow all ablastic recommendations.
During cryodestruction, the effect is exerted by means of a low temperature.
Today, oncology allows three ways to treat tumors. Radiation therapy involves the effect of radiation on the cause of a malignant tumor. Chemotherapy is defined as medical treatment. Such drugs are characterized by a destructive effect on tumor cells. The surgical method of treatment eliminates the formation with the help of an operation.
There are such types of pathologies that cannot be cured by only one of the listed methods. For this reason, a combination is often used.
Laser surgery for malignant tumor
To successfully perform oncology operations, specialist needs to know exactly where malignant tumor is located. This helps to create free access to the malignant neoplasm. Unfortunately, there are certain contraindications for this operation. These include various heart diseases, endocrine pathologies, persistent hypertension.
The flexible laser diagnostics of a malignant tumor using an endoscope allows to accurately examine the tissues inside the body. The device is equipped with an optical ultra-thin fiber that transmits light beams to illuminate the organ from inside for projection of an image onto video camera.
Laser photooculation is suitable for the treatment of several types of cancers, similar to the hyperthermia method for shrinking tumors and eliminating cancer cells. During the operation, laser fiber is placed directly into a malignant tumor, then beam light heats up the cells affected by cancer and destroys their structure.
Photodynamic therapy is characterized by the additional intravenous administration of photosensitizing drug. After some time, the drug is absorbed by the cells affected by the cancer. The laser beam activates an agent to effectively kill cancer cells.
So, laser procedures have several advantages:
accuracy (minimal trauma, in comparison with scalpel cut);
low threshold of pain syndrome after surgery;
faster healing;
less time spent on the operation.
The disadvantages are the risk of misuse of laser equipment, so be serious about choosing a clinic and your doctor.
During the operation to get rid of a malignant tumor, the oncologist can understand how realistic it is to remove tumor. There are certain reasons why it is not possible to completely remove malignant tumor. In this case, oncologists take measures to partially get rid of the tumor. With these procedures, the volume of the malignant tumor becomes smaller over time. After the operation is performed, specialist will prescribe further treatment that is appropriate for patient. The operation and method of recovery is individual for each patient.
Modern medicine has many ways to get rid of a malignant tumor. There is no universal way. Therefore, each individual case is considered individually. Much depends on the stage of development of the malignant tumor, concomitant diseases, the spread of the oncological process and many other factors. For the effect of the treatment to be as effective as possible, it is imperative to adhere to all the recommendations given to patient by his attending physician. In this case, relapse can be avoided and recovery can be achieved. After the operation, you need to undergo a second examination after a certain period of time, also prescribed by the attending physician. This allows patient to check condition and track recovery. If malignant tumor is found again, additional procedures are prescribed. For these reasons, it is important to undergo timely examinations so that oncologists can remove malignant neoplasm in time without spreading it to other vital organs of the body.
-
Signs of Diseases
Long-term non-healing skin ulcers
Inflammatory processes
Benign skin tumors
Skin diseases (eczema, psoriasis, lichen, etc.)
Scars after burns, wounds, frostbite
-
Types of Skin Lesions
Lipoma
Mole (nevus)
Papilloma
Hemangioma
Fibroma
Lymphangioma
Neurofibroma
Examination is the most obvious and simplest way to suspect a tumor. If you are worried that you are developing skin cancer, show the unusual area to doctor. He/she will compare suspicious mole or sore to other pigment cell clusters. If there are grounds for concern, doctor will prescribe additional diagnostic methods.
Laboratory Methods. The human eye is not always able to distinguish skin cancer from a benign tumor or other non-hazardous formation. Therefore, for a more accurate diagnosis, oncologists and dermatologists use a dermatoscope - a device that allows you to see the structure of a neoplasm in detail, in polarized light. For the final confirmation of the nature of the tumor, biopsy is used, in which the doctor, using a needle, tweezers or scalpel, takes a small section of patient's tissue from the affected area in order to examine it under a microscope in laboratory. Nowadays, confocal laser scanning microscopy is gaining popularity, which does not require trauma to the skin: this is especially important when tumor is located in open areas of the body.
Instrumental methods. Ultrasound and tomography are needed to assess the size of the tumor and to detect possible metastases. The most reliable type of clarifying diagnostic examination for skin cancer is positron emission tomography: with it, a radiopharmaceutical is injected into the human body, which accumulates in tumor cells and during scanning allows doctor to see the parts of the body affected by cancer. They are displayed on tomogram as glowing spots.
There are a number of causes and risk factors that play a significant role in the onset and development of skin cancer:
Skin cancer usually develops against background of previous skin changes.
There are so-called precancerous diseases: xeroderma pigmentosa, Bowen's disease, Paget's disease and some others.
Long-term exposure to the sun's ultraviolet rays.
Prolonged thermal exposure, burns.
Chemical, mechanical injuries (occupational hazards that can cause skin cancer are: resin, tar, dyes, soot, fuels and lubricants, etc.).
The presence of chronic inflammatory skin processes, chronic ulcers, fistulas, scars.
Dystrophic changes in the skin.
Anomalies of development and epithelial deformities (nevi, atheromas, dermoid cysts).